Understanding PCOS: Causes, Symptoms, and Modern Treatment Options
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is one of the most common hormonal disorders affecting individuals of reproductive age. Despite how widespread it is — impacting roughly 1 in 10 women worldwide — many people go undiagnosed for years, struggling with confusing symptoms and uncertainty about their fertility and long-term health.
This article explains what PCOS is, who it affects, and the treatment options available to help manage its symptoms and support a healthy reproductive system.
What is PCOS?
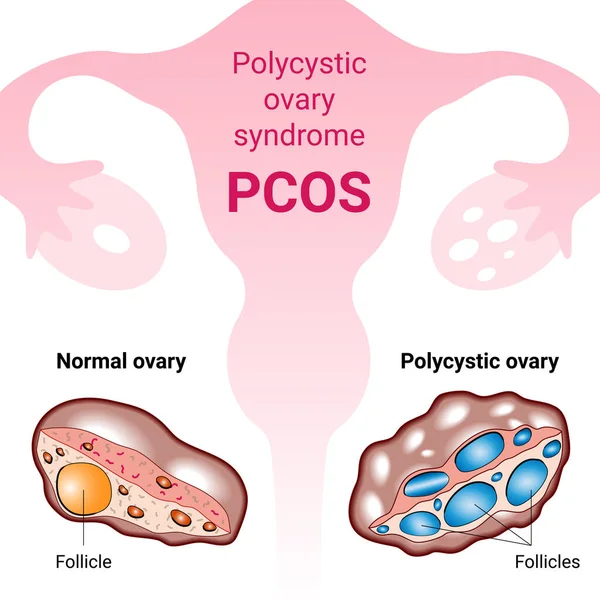
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome is a hormonal disorder characterized by an imbalance of reproductive hormones. The ovaries may become enlarged and contain small fluid-filled sacs (called cysts), which can affect regular ovulation.
The exact cause of PCOS is still unknown, but several factors seem to contribute to its development, including:
-
Insulin resistance
-
Genetic predisposition
-
Low-grade inflammation
-
Higher androgen (male hormone) levels
Who Can Experience PCOS?
PCOS primarily affects individuals assigned female at birth during their reproductive years — typically from adolescence through menopause. However, symptoms often begin soon after the first menstrual cycle and may become more noticeable over time.
Anyone can develop PCOS, but you’re at higher risk if:
-
You have a family history of PCOS
-
You are overweight or obese
-
You have insulin resistance or Type 2 diabetes
-
You experience irregular menstrual cycles
It’s also important to note that PCOS does not discriminate by race or ethnicity — it’s found globally, although the symptoms and severity may vary.
Common Symptoms of PCOS
PCOS can present a wide range of symptoms, which is one reason it often goes undiagnosed. Common signs include:
-
Irregular or missed periods
-
Excess hair growth (hirsutism), especially on the face, chest, or back
-
Acne or oily skin
-
Weight gain or difficulty losing weight
-
Thinning hair or hair loss on the scalp
-
Darkening of skin in certain areas (such as the neck or underarms)
-
Difficulty getting pregnant
These symptoms are caused by hormonal imbalances, particularly elevated levels of androgens and insulin.
How is PCOS Diagnosed?
There’s no single test for PCOS. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of:
-
Medical history and symptom review
-
Pelvic exam
-
Blood tests to check hormone levels and insulin resistance
-
Ultrasound to examine the ovaries and uterine lining
A person must usually meet at least two out of three criteria: irregular periods, signs of elevated androgens, and polycystic ovaries seen on ultrasound.
PCOS and Fertility
One of the most distressing aspects of PCOS for many women is its impact on fertility. Because the condition can interfere with ovulation, it may make it harder to conceive naturally. However, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome is one of the most treatable causes of infertility.
Many people with PCOS go on to have successful pregnancies — sometimes with lifestyle changes alone, and sometimes with medical support such as ovulation-inducing medications or IVF.
Treatment Options for PCOS
Although PCOS cannot be “cured,” its symptoms can be effectively managed with the right combination of lifestyle changes and medical treatments. Here are some of the most common options:
1. Lifestyle Modifications
-
Weight management: Losing just 5–10% of body weight can significantly improve hormone levels and menstrual regularity.
-
Diet: A balanced, low-sugar, anti-inflammatory diet helps regulate insulin and hormone levels.
-
Exercise: Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and supports weight control.
2. Medications
-
Birth control pills: Help regulate periods and reduce excess hair growth and acne.
-
Metformin: Improves insulin resistance and may help with weight loss and ovulation.
-
Clomiphene (Clomid) or Letrozole: Used to stimulate ovulation in women trying to conceive.
-
Anti-androgens: Such as spironolactone, can reduce unwanted hair and acne.
3. Fertility Treatments
For those who do not respond to ovulation medications, assisted reproductive technologies like IVF (In Vitro Fertilization) may be recommended. Many fertility clinics specialize in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome cases and offer tailored protocols to support successful pregnancies.
Long-Term Health Concerns with PCOS
PCOS isn’t just a reproductive issue — it can affect your health long-term if left unmanaged. Complications may include:
-
Type 2 diabetes
-
Heart disease
-
Endometrial cancer
-
Sleep apnea
-
Mental health challenges such as anxiety or depression
That’s why early diagnosis and proactive management are so important.
Final Thoughts
If you’re experiencing irregular cycles, acne, weight gain, or unexplained fertility issues, it’s worth speaking with a healthcare provider about Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. With early diagnosis and the right treatment plan, symptoms can be controlled, and long-term health risks reduced.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome may be complex, but it’s manageable — and with the right care, you can take control of your body, your fertility, and your future.
For any of your fertility problems, please do not hesitate to contact us. At Fertility Solutions we pride ourselves with the excellent tailored personal care we provide to our patients for their specific needs. A team member will contact you as soon as we get your message, and construct a personal treatment plan for your fertility problems in the country of Cyprus. You can also contact our clinics directly through the links below.
Cyprus Crown IVF Contact: https://en.cypruscrownivf.com/contact
Cyprus American IVF Contact: https://www.cyprusamericanivf.com/contact-us/
Dr. Halil Ibrahim Tekin (Dr. HIT) Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/@dr.halilibrahimtekin1715
Cyprus American IVF Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/@AmerikanTupBebekMerkezi