Understanding Thalassemia: Symptoms, Causes, Treatments, and Family Planning
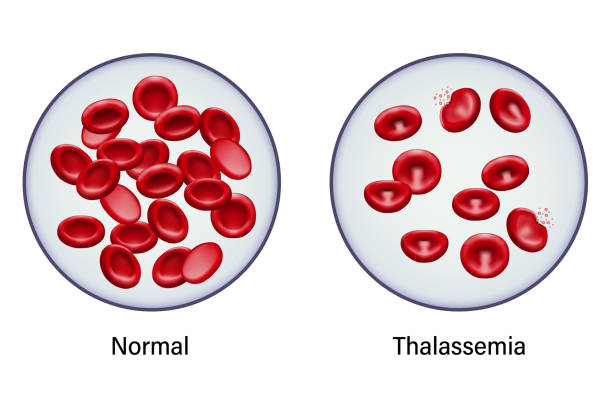
Thalassemia is a group of inherited blood disorders characterized by the body’s inability to produce sufficient hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body. This condition can significantly impact a person’s health and quality of life. In this article, we’ll explore the symptoms, causes, and treatments of thalassemia, and address the important question of whether individuals with this disease can have children.
What is Thalassemia?
Thalassemia is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder, which means that a person must inherit two defective genes—one from each parent—to develop the condition. There are two main types of this condition: alpha thalassemia and beta thalassemia, named for the types of hemoglobin chains affected.
- Alpha: This type results from mutations in the alpha-globin gene, which is crucial for producing alpha-globin chains that make up part of hemoglobin. There are four alpha-globin genes (two on each chromosome 16), and the severity of alpha thalassemia depends on how many of these genes are affected.
- Beta: This type results from mutations in the beta-globin gene, responsible for producing beta-globin chains. There are two beta-globin genes (one on each chromosome 11), and the severity of beta thalassemia is influenced by the nature and number of these mutations.
Symptoms
The symptoms of thalassemia can vary depending on the type and severity of the disorder. Here’s a breakdown of common symptoms:
- Mild Thalassemia: Individuals may experience few or no symptoms. In some cases, the condition is only detected through routine blood tests.
- Moderate to Severe Thalassemia: Symptoms can include:
- Anemia: Fatigue, weakness, and pale skin.
- Enlarged Spleen and Liver: Pain or discomfort in the upper left side of the abdomen.
- Bone Deformities: Particularly in the face and skull, due to increased marrow production.
- Delayed Growth: In children, thalassemia can lead to delayed physical development.
- Shortness of Breath: Due to reduced oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes caused by increased breakdown of red blood cells.
Causes
Thalassemia is caused by genetic mutations that affect the production of hemoglobin. These mutations can occur in the alpha-globin or beta-globin genes, leading to insufficient or abnormal hemoglobin. The disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, meaning that both parents must carry the gene mutation for their child to develop the disease.
- Alpha Thalassemia: Caused by deletions or mutations in one or more of the alpha-globin genes.
- Beta Thalassemia: Caused by point mutations or deletions in the beta-globin genes.
Treatments
Treatment for thalassemia depends on the severity of the condition and can include:
- Regular Blood Transfusions: For moderate to severe cases, regular transfusions of red blood cells are required to maintain adequate hemoglobin levels. This treatment helps to manage symptoms but can lead to iron overload, requiring additional treatment.
- Iron Chelation Therapy: To address iron overload from repeated blood transfusions, patients may be prescribed iron chelators, medications that help remove excess iron from the body.
- Folic Acid Supplements: Folate is essential for red blood cell production, and supplements can help in managing symptoms.
- Bone Marrow or Stem Cell Transplant: In some cases, a bone marrow or stem cell transplant may be considered as a potential cure. This procedure involves replacing the defective bone marrow with healthy marrow from a donor.
- Gene Therapy: Research into gene therapy aims to correct the genetic mutations responsible for thalassemia. Although still experimental, it holds promise for the future.
- Supportive Care: This includes pain management, growth monitoring in children, and regular follow-ups with healthcare providers to monitor and manage the condition effectively.
Can People with Thalassemia Have Babies?
Having children is a significant concern for many individuals with this condition, especially those with severe forms of the condition. The ability to have children and the associated risks depend on several factors:
- Genetic Counseling: Couples where one or both partners have the condition should seek genetic counseling. This process helps assess the risk of passing the condition to their children and provides information on reproductive options.
- Preconception Planning: For individuals with thalassemia, planning ahead is crucial. This includes managing their own health optimally before conception and understanding the genetic risks involved.
- Reproductive Options:
- Natural Conception: It is possible for individuals with this condition to conceive naturally, but there is a risk of passing the disorder to the child. Genetic counseling can help assess this risk.
- Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD): For those undergoing IVF, PGD can be used to screen embryos for thalassemia before implantation, reducing the risk of passing the condition to the child.
- Prenatal Testing: If a pregnancy occurs, prenatal testing such as chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis can determine if the fetus has inherited thalassemia.
- Management During Pregnancy: For pregnant women with thalassemia, careful monitoring and management are essential to ensure both maternal and fetal health. Regular consultations with a specialist in maternal-fetal medicine may be recommended.
Conclusion
Thalassemia is a serious genetic disorder that requires careful management and treatment. Advances in medical science offer hope and improved quality of life for those affected by the condition. With appropriate medical care, support, and planning, individuals with this condition can manage their health effectively and make informed decisions about family planning. If you or a loved one has suffering from this condition, seeking guidance from healthcare professionals and genetic counselors can provide valuable support and information tailored to your specific needs. Lastly, check out this article for more information about thalassemia.
Cyprus Crown IVF Contact: https://en.cypruscrownivf.com/contact
Cyprus American IVF Contact: https://www.cyprusamericanivf.com/contact-us/
Dr. Halil Ibrahim Tekin (Dr. HIT) Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/@dr.halilibrahimtekin1715
Cyprus American IVF Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/@AmerikanTupBebekMerkezi